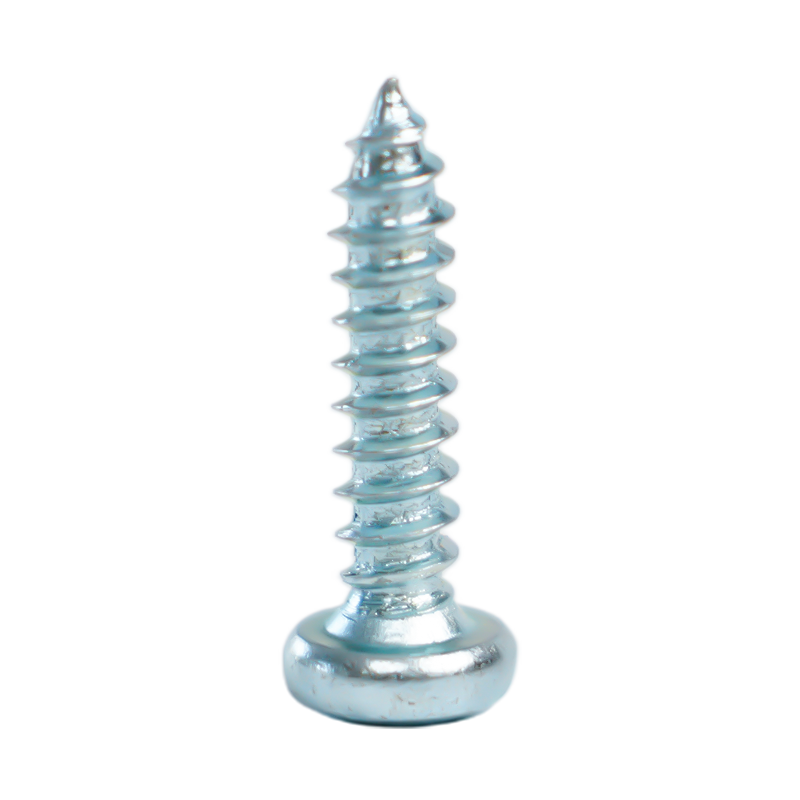
In the vast world of fasteners, carbon steel screws stand as a fundamental and versatile component, essential for countless construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. Their strength, affordability, and wide availability make them a go-to choice. However, not all carbon steel screws are created equal, and selecting the right one is critical for the longevity and safety of any assembly. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the specifics of carbon steel screws, addressing common questions and advanced selection criteria to empower professionals and enthusiasts alike with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding Carbon Steel Screws: Composition and Advantages
Carbon steel screws are fasteners made from an iron-carbon alloy, where carbon is the primary hardening element. The percentage of carbon significantly influences the screw's properties, leading to different grades suitable for various applications.
Key Characteristics and Benefits
- High Tensile Strength: They offer excellent load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for structural connections.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to stainless steel or specialty alloys, carbon steel provides a superior strength-to-price ratio.
- Wide Availability: They come in an extensive range of sizes, head types, and drives, from common Phillips to Torx.
- Surface Treatment Compatibility: They readily accept coatings like zinc plating, galvanization, or black oxide for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Common Grades of Carbon Steel for Screws
Different grades denote varying levels of carbon content and mechanical properties. For instance, low-carbon steel (like Grade 2) is softer and more ductile, while medium/high-carbon steel (like Grade 5 or 8) is stronger and more brittle. Selecting the correct grade is the first step in ensuring a successful application.
Navigating the Selection: Answering Your Critical Questions
Choosing the right screw involves more than just size. We address five pivotal queries that guide users toward the optimal fastener for their specific needs.
carbon steel screw vs stainless steel strength
A common misconception is that stainless steel is inherently stronger. In reality, when comparing tensile strength, many grades of carbon steel screws outperform their stainless counterparts. The primary advantage of stainless steel lies in its corrosion resistance, not its absolute strength. For high-strength applications without severe corrosive environments, carbon steel is often the superior mechanical choice.
| Property | Carbon Steel Screw (Grade 5) | Stainless Steel Screw (304) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Higher (approx. 120,000 psi) | Lower (approx. 80,000 psi) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (requires coating) | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Primary Use Case | Structural, indoor, coated outdoor | High-moisture, chemical, food-grade |
best coating for outdoor carbon steel screws
For outdoor use, bare carbon steel will rust quickly. The right coating is essential for longevity. Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) provides a thick, sacrificial layer of zinc, offering decades of protection in harsh environments. Mechanical galvanizing is excellent for threaded parts. For less severe conditions, a high-quality zinc plating with a supplemental chromate conversion coating (like yellow or black zinc) can be sufficient and more cost-effective.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Maximum protection for fencing, structural steel, and marine applications.
- Mechanical Galvanizing: Excellent corrosion resistance without compromising thread fit.
- Zinc Plating with Sealer: A good balance of cost and protection for decking and outdoor furniture.
high tensile carbon steel screw specifications
High-tensile carbon steel screws, such as those meeting Grade 8 or SAE J429 specifications, are engineered for critical, high-stress applications. Key specifications include a minimum tensile strength of 150,000 psi for Grade 8, marked by six radial lines on the head. They are typically made from medium carbon alloy steel, quenched and tempered. Understanding these specifications—including proof load, yield strength, and hardness—is vital for engineering and construction projects where failure is not an option, such as in automotive suspensions or heavy machinery.
carbon steel screw corrosion resistance methods
Since carbon steel is susceptible to oxidation, enhancing its corrosion resistance is a science in itself. Methods range from simple barriers to advanced electrochemical protection.
| Method | Process | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| Electroplating (Zinc, Nickel) | Electrolytic deposition of a metal layer. | Good to Very Good (Barrier) |
| Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Immersion in molten zinc. | Excellent (Barrier & Sacrificial) |
| Phosphating & Oil | Creates a crystalline phosphate layer that holds oil. | Fair (Barrier, for indoor/mild conditions) |
| Powder Coating | Electrostatically applied polymer coating, then cured. | Excellent (Barrier, with aesthetic choice) |
carbon steel screw for heavy duty construction
In heavy-duty construction, screws must withstand immense shear and tensile forces, vibration, and dynamic loads. Carbon steel screw for heavy duty construction applications are not just about size but about material grade, heat treatment, and design. Lag screws (lag bolts), large structural wood screws, and hex cap screws made from high-tensile carbon steel are common. They often feature aggressive, deep threads and are installed with precise torque specifications to ensure clamping force without stripping. For timber framing or steel-to-wood connections, specially engineered screws with alternating thread designs or self-drilling tips are used[1].
Specialized Applications and Technical Insights
Beyond general use, carbon steel screws are engineered for specific challenges.
Thread-Forming and Thread-Cutting Screws
For metals or dense materials, standard screws may not suffice. Thread-forming screws displace material to create a mating thread, ideal for ductile metals like aluminum. Thread-cutting screws, which have a cutting edge, are used for brittle materials like cast iron or plastic, removing material to form the thread[2].
Importance of Drive Type and Head Style
The drive system (e.g., Phillips, Slotted, Torx, Square) impacts torque transfer and cam-out risk. Torx and Square drives allow for higher torque application with less slippage. Head style (flat, pan, hex, oval) affects finish, clearance, and load distribution.
Wuxi Sharp Metal Products: Three Decades of Fastening Excellence
Since our official establishment in 1993, Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd. has grown into a professional enterprise dedicated to the production and trade of high-quality fasteners. Our foundation is built on a 6000-square-meter factory equipped with over 100 machines, supporting an annual output of approximately 2000 tons and maintaining an inventory exceeding 800 tons to ensure timely delivery.
Our core philosophy of "quality first, reputation first" drives every aspect of our operation. We produce a comprehensive range of screws, including the essential carbon steel screws, stainless steel self-tapping screws, wood screws, and specialized fasteners for drywall, fiber, and cement. Our expertise extends into the door and window accessories trade, a sector we have served since 2000, providing reliable components for both engineering and home decoration systems.
Our commitment is realized through a strict quality assurance system, continuous employee training, and comprehensive management practices. We understand that the correct carbon steel screw for heavy duty construction or the optimal best coating for outdoor carbon steel screws can define a project's success. By leveraging technology and maintaining innovation, we ensure our products meet the evolving demands of the market, providing superior value to our customers worldwide. Our integrity-based approach has earned us a respected reputation among domestic and international peers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I use carbon steel screws for outdoor furniture?
Yes, but only if they have a suitable protective coating. Bare carbon steel will rust. Choose screws with hot-dip galvanizing or high-quality zinc plating for lasting outdoor use.
2. How do I identify the grade of a carbon steel screw?
Look for markings on the screw head. For instance, three radial lines indicate SAE Grade 5, and six lines indicate Grade 8. Unmarked screws are typically lower-grade, mild steel.
3. What is the main disadvantage of carbon steel screws?
Their susceptibility to corrosion is the primary drawback. Without proper coating or in corrosive environments (salty, acidic, or consistently wet), they will degrade over time.
4. Are high-tensile carbon steel screws always brittle?
Not necessarily. While increasing strength can reduce ductility, proper heat treatment (quenching and tempering) in grades like Grade 8 provides an excellent balance of high strength and good toughness to resist shock loads.
5. Why might a professional choose a carbon steel screw over stainless steel for an indoor project?
The decision often comes down to strength and cost. For structural, load-bearing applications indoors, a high tensile carbon steel screw offers greater clamping force and shear strength at a lower cost than a standard stainless steel screw, with no corrosion concerns.
References
[1] American Society of Civil Engineers. (2017). *Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE/SEI 7-16)*. Reston, VA: ASCE. (Relevant for structural screw applications in construction).
[2] Bickford, J. H., & Nassar, S. (Eds.). (2017). *Handbook of Bolts and Bolted Joints*. CRC Press. (Reference for thread-forming/cutting mechanisms and general fastener technology).

 +86-15052135118
+86-15052135118 

 Español
Español
 Get In Touch
Get In Touch