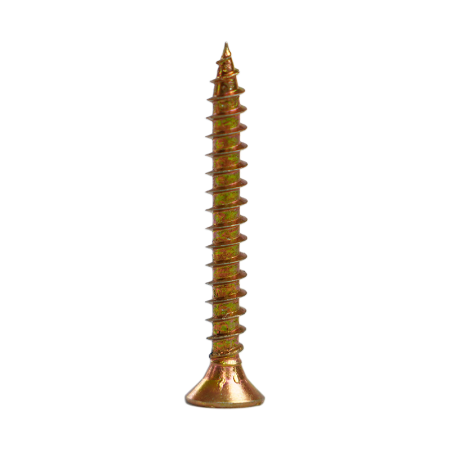
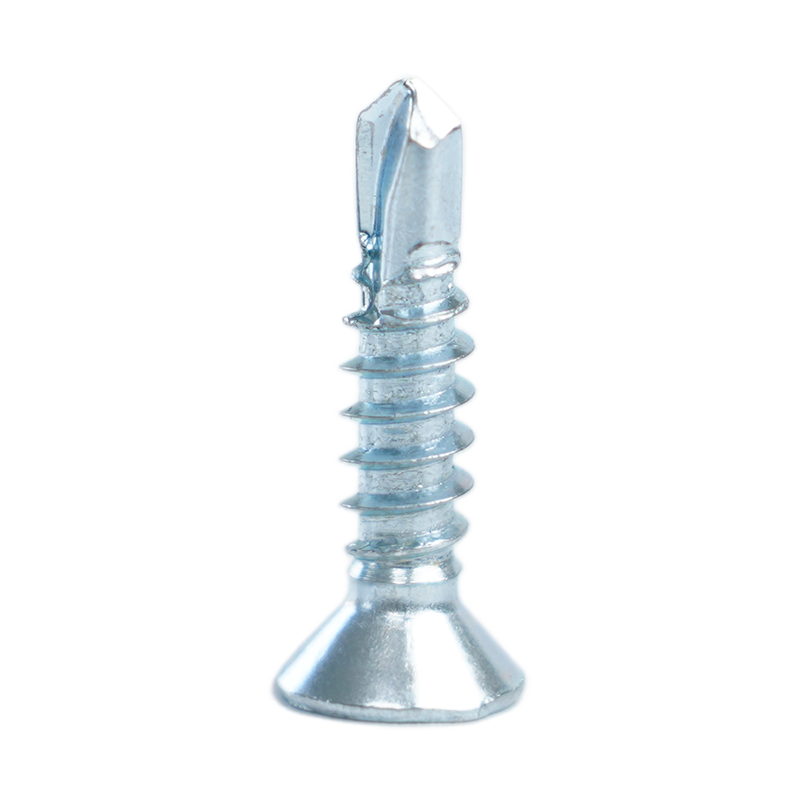
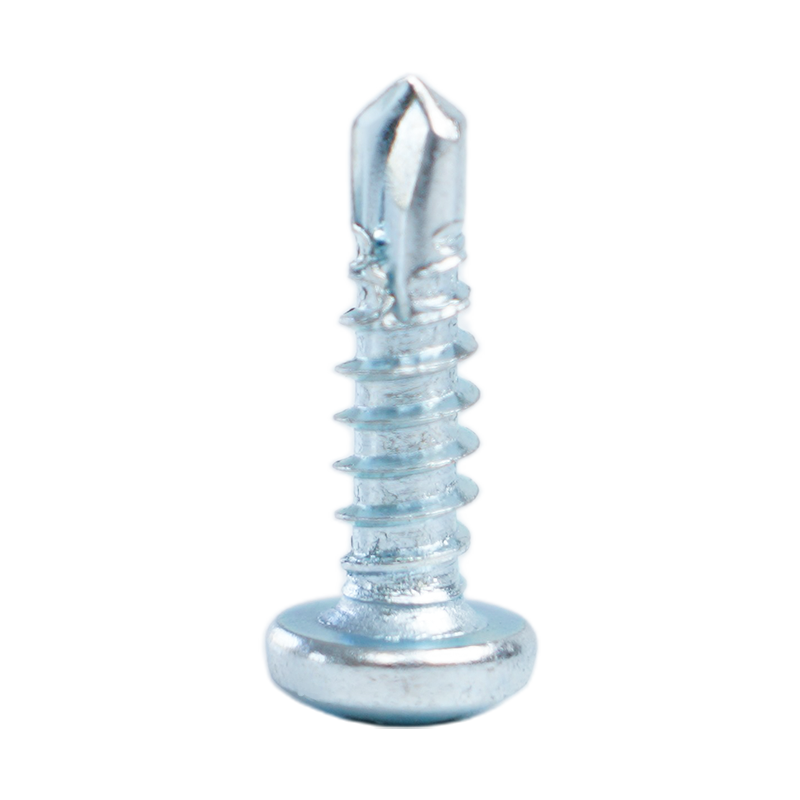
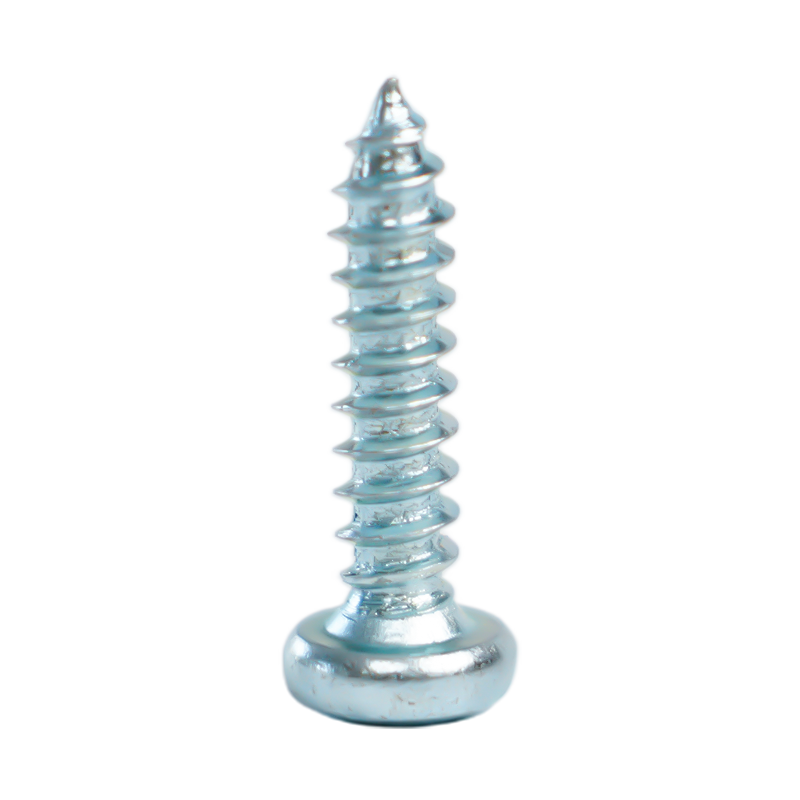
Understanding Chipboard Screws: Definition and Key Characteristics
Chipboard screws, also known as particle board screws, are specialized fasteners engineered specifically for use in manufactured wood products. These include medium-density fiberboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board. Unlike standard wood screws, chipboard screws feature unique design elements that address the particular challenges of engineered wood materials.
Critical Design Features of High-Quality Chipboard Screws
Premium chipboard screws from manufacturers like Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd incorporate several essential design elements:
- Aggressive self-tapping points that cut through dense composite materials without requiring pre-drilling in most applications
- Wide, deep threads with sharp edges that provide maximum holding power in soft, fibrous substrates
- Special thread geometry designed to remove material rather than compress it, reducing splitting risk
- Hardened steel construction with proper tempering to prevent bending or breaking during installation
- Various corrosion-resistant coatings including zinc plating, galvanization, or specialized finishes for different environments
- Precision-formed drive heads (Phillips, Pozi, or Torx) that minimize cam-out during installation
Material Composition and Manufacturing Standards
Quality chipboard screws are typically manufactured from:
- Carbon steel (most common for general applications)
- Stainless steel (for corrosive environments)
- Case-hardened steel (for maximum strength)
Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd employs strict quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process, from raw material selection to final inspection, ensuring consistent performance across production batches.
Comparing Chipboard Screws vs. Wood Screws: Key Differences
While chipboard screws and standard wood screws may appear similar at first glance, they have several critical differences that affect their performance:
| Feature | Chipboard Screws | Standard Wood Screws |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Design | Wider, deeper threads with sharper edges and greater thread spacing | Narrower, shallower threads with more gradual taper |
| Point Design | More aggressive self-tapping tip with sharper cutting edges | Less pronounced tapping point, designed more for displacement than cutting |
| Material Hardness | Typically harder steel alloys (HRC 45-50) to penetrate dense composites | Softer temper (HRC 35-40) suitable for natural wood fibers |
| Thread Angle | Steeper thread angle (approximately 30 degrees) for better chip removal | Shallower angle (approximately 20 degrees) for natural wood |
| Shank Design | Often feature partially threaded shanks to prevent material separation | Typically fully threaded for maximum grip in solid wood |
When to Use Each Type
The choice between chipboard screws and wood screws depends on several factors:
- Use chipboard screws when working with engineered wood products, especially in structural applications
- Use standard wood screws for natural wood where splitting is less of a concern
- Chipboard screws generally provide better holding power in particle board and MDF
- Wood screws may be more appropriate for visible applications where head aesthetics matter
Best Practices for Installing Chipboard Screws
Proper installation techniques are crucial for achieving optimal performance from chipboard screws while preventing material damage.
Pre-Drilling Guidelines
While chipboard screws are designed to be self-tapping, pre-drilling may be necessary in certain situations:
- When working near edges (within 25mm of panel edges) to prevent blowout
- For thicker materials (over 25mm) to reduce driving torque and prevent screw breakage
- When using larger diameter screws (#10 and above) to ease installation
- In extremely dense composite materials that may challenge even specialized screws
Recommended Drill Settings
For optimal results when driving chipboard screws:
- Use a drill/driver with adjustable torque settings
- Set clutch to mid-range initially, adjusting as needed
- Maintain a straight driving angle throughout installation
- Use moderate, consistent pressure - let the screw do the work
- For power drivers, set speed to 1500-2000 RPM for best results
Countersinking Techniques
Proper countersinking improves both appearance and performance:
- Use dedicated countersink bits matched to screw head angle
- For flush mounting, drill to depth where screw head sits slightly below surface
- In visible applications, consider using decorative caps or plugs
- For painted surfaces, countersink allows for proper filler application
Selecting the Right Chipboard Screw Size for Your Project
Choosing appropriate screw dimensions is critical for structural integrity and long-term performance.
Diameter Selection Guidelines
The ideal screw diameter depends on several factors:
- Panel thickness: Thicker materials generally require larger diameters
- Expected load requirements: Higher loads demand larger diameters
- Material density: Denser composites may need larger diameters for sufficient grip
- Edge distance: Smaller diameters allow installation closer to edges
Typical diameter recommendations:
| Material Thickness | Recommended Diameter | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 12-18mm | 3.5-4.0mm (#6-#8) | Furniture assembly, cabinet backs |
| 18-25mm | 4.0-4.5mm (#8-#10) | Shelving, structural panels |
| 25mm+ | 4.5-5.0mm (#10-#12) | Heavy-duty framing, load-bearing applications |
Length Selection Principles
Screw length should be chosen based on:
- Material thickness: Screw should penetrate at least 2/3 of bottom layer
- Joint type: Butt joints require longer screws than edge joints
- Load requirements: Higher loads benefit from deeper penetration
As a general rule, the screw should be long enough to penetrate the bottom material by at least 10mm for light-duty applications, and 15-20mm for structural connections.
Understanding Chipboard Screw Thread Types and Their Applications
Different thread patterns serve specific purposes in chipboard applications, and selecting the right type can significantly impact performance.
Primary Thread Varieties
Manufacturers like Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd typically offer several thread options:
- Coarse threads (standard): Ideal for general-purpose chipboard applications
- Fine threads: Better for denser composites and harder engineered woods
- Double-lead threads: Feature two start points for faster installation
- Hi-lo threads: Alternating high and low threads for better chip clearance
- Self-drilling points: Incorporate a drill point for metal-to-wood applications
Thread Geometry Comparison
| Thread Type | Threads Per Inch | Best For | Installation Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse | 8-10 | Standard particle board, MDF | Medium |
| Fine | 12-14 | Dense composites, edge joints | Slower |
| Double-lead | 8 (dual) | High-volume production | Fastest |
Preventing and Solving Chipboard Screw Stripping Issues
Stripping is a common problem that can compromise joint integrity and lead to structural failures.
Primary Causes of Stripping
Several factors contribute to screw stripping in chipboard applications:
- Using incorrect driver bits: Worn or mismatched bits increase cam-out risk
- Over-tightening: Excessive torque damages both screw and material
- Poor quality fasteners: Soft metal or imprecise head geometry strips easily
- Material factors: Overly dense or inconsistent substrates increase stripping risk
- Driver speed: Too high RPM can generate excess heat and soften metal
Solutions for Stripped Screws
When stripping occurs, several repair options exist:
- Extraction methods:
- Rubber band between bit and screw head
- Specialized extraction bits
- Left-hand drill bits
- Repair techniques:
- Fill hole with epoxy/wood filler and redrill
- Use larger diameter screw in new location
- Install threaded insert for permanent repair
Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd: Your Trusted Chipboard Screw Manufacturer
With decades of experience in fastener manufacturing, Wuxi Sharp Metal Products Co., Ltd has established itself as a reliable global source for high-quality chipboard screws and other specialized fasteners.
Our Manufacturing Capabilities and Expertise
Our 6,000m² production facility in Yanqiao Industrial Park features:
- 100+ specialized machines including cold heading equipment, thread rollers, and heat treatment systems
- 800+ tons of raw material inventory ensuring consistent supply
- Annual production capacity exceeding 2,000 tons
- Dedicated R&D team continuously improving screw designs
- Advanced quality control laboratory with testing equipment
Quality Assurance and Certifications
We maintain rigorous quality standards through:
- ISO 9001 certified quality management system
- Raw material chemical composition testing
- Dimensional inspections at multiple production stages
- Mechanical performance testing (tensile strength, torque resistance)
- Surface treatment quality verification
- Batch traceability for quality control
Product Range and Custom Solutions
Our comprehensive chipboard screw offerings include:
- Standard chipboard screws in various sizes and finishes
- Specialty designs for specific applications
- Custom configurations based on customer requirements
- Various head styles (flat, oval, round, wafer)
- Multiple drive types (Phillips, Pozi, Torx, square)
- Different coatings (zinc, galvanized, black oxide)
Global Reach and Industry Applications
Since 2000, we've supplied chipboard screws for diverse industries worldwide:
- Furniture manufacturing
- Cabinetry and millwork
- Construction and building materials
- DIY and retail packaging
- OEM applications
Our products meet international standards including DIN, ANSI, and JIS specifications, ensuring global compatibility.

 +86-15052135118
+86-15052135118 

 Español
Español
 Get In Touch
Get In Touch